ScriptRunner Blog
Handling Events with PowerShell and WMI
Inhaltsverzeichnis

In this blog post, we will have a look at WMI eventing. You’ll learn about the two types of WMI events (extrinsic and intrinsic) and how you can handle both with PowerShell.
This is part 2 of our series „Handling events with PowerShell“. Click here, for the first part of the series Handling Events with PowerShell and .NET
What is WMI Eventing
WMI stands for Windows management instrumentation. WMI is the Microsoft implementation of CIM (Common Information Model). CIM is a standard from DMTF (Distributed Management Task Force) which defines how to represent system information. In short CIM is a vendor neutral model used to represent system information. Microsoft’s implementation of CIM is known as WMI.
One can think of WMI as a database which stores information about the system. But how can we view this information and where is it stored? On a Windows system you can find WMI located at
C:\Windows\System32\wbem\Repositoryas shown in fig. 1 below.
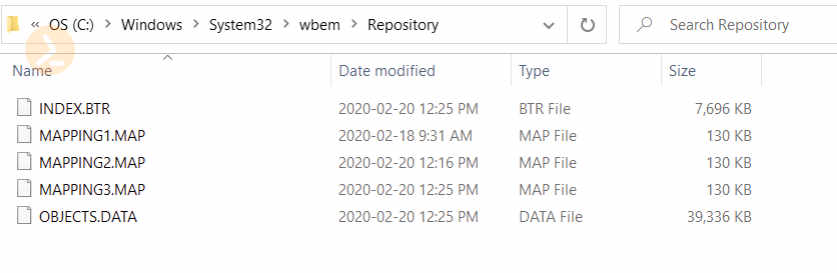
Figure 1: WMI location
Wmic was the tool of choice to interact with WMI, but it has since been deprecated. Although it’s still available on Windows system and if you try to use it you will receive a message like the one shown in fig. 2.
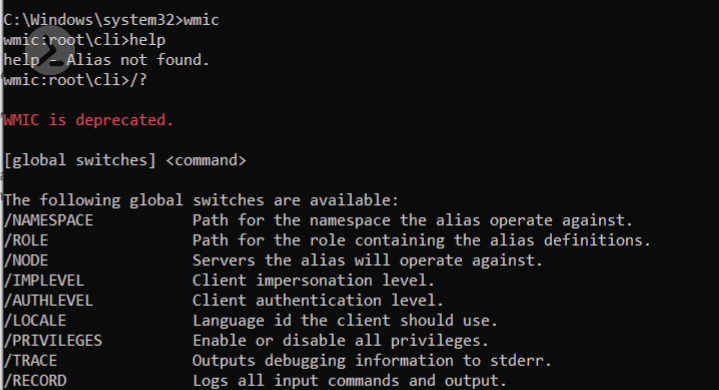
Figure 2: Deprecated WMIC command
Moving forward Microsoft recommends using PowerShell to interact with WMI. PowerShell has inbuilt cmdlets to interact with WMI. These were called “WMI cmdlets” however they have been deprecated in favor of CIM cmdlets since PowerShell version 3. In this article we will be using CIM cmdlets. In order to view available CIM cmdlets we will use our favorite cmdlet called Get-Command
Get-Command -noun *CIM*Get-CimAssociatedInstance Get-CimClass Get-CimInstance Get-CimSession Invoke-CimMethod New-CimInstance New-CimSession New-CimSessionOption Register-CimIndicationEvent Remove-CimInstance Remove-CimSession Set-CimInstance
For the sake of completeness lets also take a look at the WMI cmdlets available in PowerShell, using the following cmdlet
Get-Command -noun *wmi*
resulting in the following list:
Get-WmiObject Invoke-WmiMethod Register-WmiEvent Remove-WmiObject Set-WmiInstance
It’s clear to see, that there are more CIM cmdlets than WMI cmdlets. CIM cmdlets are the future hence we won’t be talking about WMI cmdlets anymore.
As mentioned before, WMI is used to represent system information but how does it store this information? The answer is simple: WMI uses hierarchical structure starting from namespaces to store and manage system wide information. These namespaces have various classes underneath them where each class represents specific system information. So, for example the WIN32_DiskDrive class is used to represent information on disk drive. If the system has a disk drive, then this class will have an object with properties and methods representing the disk drive for that system.
We can use the Get-CIMInstance cmdlet to interact with WMI and view this object. The Get-CIMInstance requires class name as one of the parameters. As we can see in fig. 3, the Get-CIMInstance cmdlet returns the object for Win32_DiskDrive class. This object has properties such as DeviceID, Caption, Partitions, Size, Model etc.
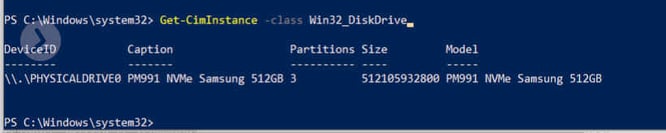
Figure 3: Win32_DiskDrive Objects
Let’s take another example: suppose – and this is highly unlikely on modern laptop – I want information about my CD-ROM 😊. WMI has the Win32_CDROMDrive class which is used to represent CD-ROM information. Let’s use the Get-CIMInstance cmdlet to get the object.
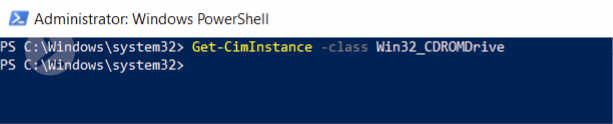
Figure 4: : No objects for Win32_CDROMDrive
Since I use a modern laptop, I don’t have a CD-ROM hence our cmdlet did not return any object (as shown in fig. 4).
Two interesting observations here: even though CD-ROM object does not exist we can still inquire about the object without receiving an error, secondly even if CD-ROM is not present on the system WMI still have the Win32_CDROMDrive class available.
Similarly, we can inquire WMI for information on all the running processes on a system as shown below
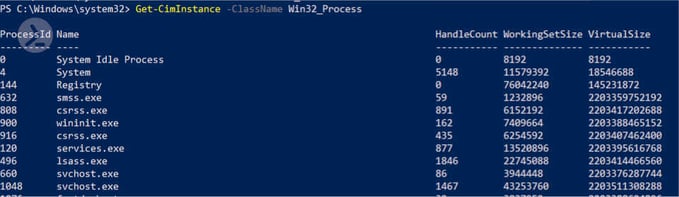
Figure 5: Objects for Win32_Process class
If you want more information or want to explore what other classes are available in WMI
Microsoft Documentation on WMI is a good place to start.
Apart from representing system information, WMI also provide a powerful feature called “eventing”. Essentially WMI provide the capability to monitor system wide events and notify user. There are two types of events in WMI Intrinsic and Extrinsic events.
Intrinsic WMI Events
Intrinsic events are tied closer to WMI itself. They are triggered in response to changes in WMI structure. For example, if a new process is created on the system it will result in a new instance being created for the WIN32_Process class, this will result in an event of type __Instancecreationevent. Another example would be a new class being created in WMI this will result in an event of type __ClassCreationEvent.
Just like everything in WMI is represented as objects, events are represented as objects too and each event type has an associated class as listed below. However, one thing to keep in mind is that these objects representing an event are short-lived hence we use pooling when we are creating our event filter else we can miss these objects being created.
Following are different types of Intrinsic events:
__NamespaceOperationEvent, __NamespaceModificationEvent, __NamespaceDeletionEvent, __NamespaceCreationEvent, __ClassOperationEvent __ClassDeletionEvent, __ClassModificationEvent, __ClassCreationEvent, __InstanceOperationEvent, __InstanceCreationEvent, __MethodInvocationEvent, __InstanceModificationEvent, __InstanceDeletionEvent, __TimerEvent
Extrinsic Events
Extrinsic events are generated based on underlying OS level changes. This is a major difference while intrinsic events are looking for changes within WMI structure, extrinsic events are looking for changes outside WMI at OS level. For example, Computer shutdown event is an OS level event hence its classified as Extrinsic event. Extrinsic events do not require pooling.
Following are different types of extrinsic events:
Win32_ComputerShutdownEvent, Win32_IP4RouteTableEvent, Win32_ProcessStartTrace, Win32_ModuleLoadTrace, Win32_ThreadStartTrace, Win32_VolumeChangeEvent, Msft_WmiProvider*, RegistryKeyChangeEvent, RegistryValueChangeEvent
In order to work with these events, we need to understand the concept of filters, but before we talk about filter, we take a quick segue to WQL.
WQL is WMI query language and is like SQL. It uses the same syntax as SQL to query WMI for information.
More information on WQL can be found at on Microsoft Documentation site.
Using WQL for event filters
We use WQL to create filters for events. A filter can be thought of as a search condition to look for particular event.
Let’s take an example: suppose we want to capture a new process creation event, particularly the calculator process. In order to do this, we need to create a WQL query for defining the filter for capturing this event. In this case we want to capture the creation of a new instance for WIN32_Process class where process name is „calc.exe“, once we capture this event, we want to take an action. For this specific example we want to print “WMI is awesome”.
Let’s start by defining our filter using WQL, in this case we are looking for instance creation event hence our query starts with
Select * from __InstanceCreationEvent
Next, since this is an Intrinsic Event we need to define the pooling interval hence our WQL query becomes
Select * from __InstanceCreationEvent within 10
Next, we need to define which class instance we are looking for? So, we add that information to our query
Select * from __InstanceCreationEvent within 10 where TargetInstance ISA “Win32_Process”
Next, we need to be specific in what type of instance we are looking for, in this case we are looking for a process instance with name property “calc.exe” hence our WQL query end up looking like below.
Select * from __InstanceCreationEvent within 10 where TargetInstance ISA “Win32_Process” and TargetInstance.Name like “%calc%”
Now that we have our filter defined, we need to subscribe for the event and define the action to take once the event is observed.
In order to do this, we would use the Register-CimIndicationEvent cmdlet. The Register-CimIndicationEvent cmdlet requires following parameters to subscribe for an event (as shown in Fig. 6)
-wqlQuery -SourceIdentifier -Action
The -SouceIdentifier parameter can be supplied with a user defined name.
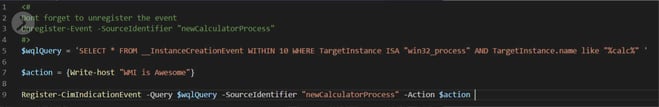
Figure 6: WMI temporary event subscription
If the cmdlet is successful you will receive a message like the one show in fig. 7. It indicates that we have successfully subscribed to the event.
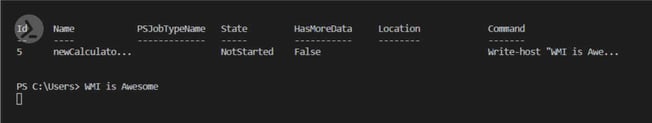
Figure 7: Successful event subscription
As you can observe, once I launch the calc.exe process I get the message “WMI is Awesome” printed on the screen.
This works fine until you exit the PowerShell command prompt. Since this is a temporary event subscription it is dependent on the lifetime of the process under which it was created, in our case the PowerShell command prompt. Once we exit the parent process we lose our subscription.
WMI provides permanent WMI event subscription which makes our subscription permanent and persist system reboot.
This brings us to the next important concept we need to understand before we start building permanent event subscriptions. There are three major concepts to understand
- Event Filter
- Event Consumer
- Event Filter to Consumer binding
Event filters
We have seen event filters before in our last example, as previously mentioned Event filters are used to subscribe for particular events. You can think of them as search condition to look for particular events. But there is a difference: while in our last example we defined the filter and supplied it in the form of WQL query to the Register-CimIndicationEvent cmdlet, in case of permanent event subscription we will create our filter in WQL, however we will then initialize an object of class __EventFilter and supply our filter as one of the properties of this object.
Event consumer
Once our event filter matches the criteria we would like to take certain action like we did in our example for temporary event subscription. For permanent event subscription we have five action types provided by five different consumer classes to choose from.
- LogFileEventConsumer: Writes to a log file.
- ActiveScriptEventConsumer: Execute a Script.
- NTEventLogEventConsumer: Write to Windows event log.
- SMTPEventConsumer: Send an email.
- CommandLineEventConsumer: Command line execution.
Just like in the case of Event filters once we know what action we like to take we need to initialize an object of that class and supply it with values for certain properties.
Once you have the event filter and consumer defined the only work left is to join them together, filter to consumer binding do exactly that for us. We create an object of __FilterToConsumerBinding class and supply it with values for Filter and Consumer objects.
Example: setting up permanent WMI event subscription
Let’s take an example, suppose we want to generate Event log when a user plugs in a USB device. We can easily do this using WMI eventing.
It’s a three-step process:
- We first define the Filter for an Event representing “user plugging in USB stick”
- We then define a Consumer to generate Event log when this Filter matches the Event
- Finally, Filter-to-Consumer binding joins the Event Filter with the rightful Consumer
Fig. 8 shows a schematic representation of this process.

Figure 8: Process for permanent WMI event subscription
The New-CimInstance cmdlet is used to create an instance of CIM class and can be used for creating instances on remote computer if used with CimSession parameter.
In our script we use the New-CIMInstance cmdlet to create instances for EventFilter, EventConsumer and FilterToConsumer classes.
With that said, let’s bring all of this together and create our first WMI event subscription:
Step 1: First we define our WQL query for our filter:
$WQLQuery = 'SELECT * FROM __InstanceCreationEvent WITHIN 10 WHERE TargetInstance ISA "Win32_USBControllerDevice"'
When a USB device is plugged into a system a new instance of WIN32_USBControllerDevice is created hence we are looking for an instance creation event. Now, we define our filter as shown below:
$WMIFilterInstance = New-CimInstance -ClassName __EventFilter -Namespace "rootsubscription" -Property @{Name="myFilter";
EventNameSpace="rootcimv2";
QueryLanguage="WQL";
Query=$WQLQuery
}
As you can notice we are creating an object of class __EventFilter and store it in $WMIFilterInstance variable. We also provide values for some properties of this object, the most important being Name and Query.
Step 2: Next, we define our consumer, in our case we want to generate an event log hence we create an instance of NTEventLogEventConsumer class.
$WMIEventConsumer = New-CimInstance -ClassName NTEventLogEventConsumer -Namespace "rootsubscription" -Property @{Name="USBLogging";
EventId = [uint32] 1; EventType = [uint32] 4; #EventType can have following values; Error 1, FailureAudit 16, Information 4, SuccesAudit 8, Warning 2
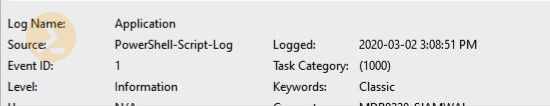
SourceName="PowerShell-Script-Log"; Category= [uint16] 1000 } #Category is never really used but can have any value and basically meant to provide more information about the event
Some things to keep in mind are the EventID and EventType properties, also the sourceName is used to define the source of the event.
Step 3: Finally, we bind our filter with the consumer.
$WMIWventBinding = New-CimInstance -ClassName __FilterToConsumerBinding -Namespace "rootsubscription" -Property @{Filter = [Ref] $WMIFilterInstance;
Consumer = [Ref] $WMIEventConsumer
}
As you can notice in order to create the filter-to-consumer binding we need to supply the object we created earlier a value for the Filter and Consumer property. You can find the complete script I’m using here in my GitHub repository
Once executed, this script creates a permanent event subscription. The next time a user plugs in a USB device you will notice an entry in the Windows Event log being created, just as shown in fig. 9 and fig. 10 below.

Figure 9: Windows Event Log
Remove an event subscription
Just a final note before we end this blog post: if we want to remove permanent event subscription, we need to execute following three commands:
Get-CimInstance -ClassName __EventFilter -namespace rootsubscription -filter "name='myFilter'" | Remove-CimInstance Get-CimInstance -ClassName NTEventLogEventConsumer -Namespace rootsubscription -filter "name='FolderWriteLogging'" | Remove-CimInstance Get-CimInstance -ClassName __FilterToConsumerBinding -Namespace rootsubscription -Filter "Filter = ""__eventfilter.name='myFilter'""" | Remove-CimInstance
The Get-CimInstance cmdlet returns the object for the class specified by using the ClassName parameter which we pass it to Remove-CimInstance cmdlet for removal. More information on GetCimInstance can be found in the Microsoft Documentation.
Conclusion
As you can notice we can leverage WMI eventing for monitoring various changes across the system. WMI is powerful technology yet remains unknown among systems administrators. PowerShell has made it easy to interact and work with WMI by providing us with useful cmdlets. I hope this article will encourage the audience to learn more about WMI and leveraging PowerShell to use this technology for interesting projects.
Full control and complete traceability
You can leverage your monitoring capabilities even more by using ScriptRunners Report/Audit DB Connector. It lets you store all your reports on script execution in one central repository and provides you with complete traceability of all processes.
Zusammenhängende Posts
14 min read
Privacy Management mit PowerShell – hier kommen die wichtigsten Funktionen von Priva auf einen Blick
Jul 16, 2024 by Damian Scoles
Kennst du Priva? Datenschutzmanagement, Datenschutzrichtlinien, Regeln und Subjektrechte-Anfragen (data subject rights...
5 min read
Happy System Administrator Appreciation Day!
Jul 3, 2024 by Matthias Jütte
Jeden letzten Freitag im Juli wird der System Administrator Appreciation Day gefeiert, einen besonderen Tag, der den...
8 min read
PowerShell 7: Was spricht für, was gegen den Umstieg?
Jun 28, 2024 by Philip Lorenz
Windows PowerShell 5.1 ist in der Regel vorinstalliert und der Standard – lohnt sich ein Wechsel auf PowerShell 7, oder...
Über den Autor:
Sonny ist ein selbsternannter PowerShell-Prediger, der in der schönen Stadt Halifax an der Ostküste Kanadas lebt. Sonny arbeitet seit mehr als 10 Jahren im Bereich Cybersecurity und hat als primärer technischer Leiter und Fachexperte bei vielen Cyber Security Assessments für verschiedene private und öffentliche Organisationen fungiert. Sonny spricht regelmäßig auf verschiedenen Sicherheitskonferenzen wie BSides, AtlSecCon, ISACA, OWASP etc.